Magnetization Transfer¶
MR voxels often contain complex microstructure with multiple different components or pools, each with unique relaxation properties. It is possible for magnetization to be transferred between these pools via several mechanisms, such as exchange of individual protons or entire molecules, or simple dipolar coupling from molecules that are in close proximity. These mechanisms can be studied in the related fields of Magnetization Transfer (MT) and Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST). QUIT contains tools for quantitative MT (qi qmt, qi ssfp_emt), CEST (qi zspec_interp, qi lorentzian) and also for processing MPM data (qi mtsat). Example nipype workflows for CEST analysis are also provided.
qi lineshape¶
A utility to sample lineshapes and write them out to files, which can then be read by qi qmt and interpolated values used instead of calculating the lineshape during fitting. This is used principally to speed up fitting the Super-Lorentzian lineshape, which takes a long time to calculate but is smoothly valued, so can be accurately approximated using interpolation.
Example Command Line
qi lineshape --lineshape=SuperLorentzian --frq_start=500 --frq_space=500 --frq_count=150 superlorentz.json
The output will be written to the file specified on the command-line (in this case superlorentz.json).
Important Options
--lineshape, -lChoose from a Gaussian, a Lorentzian or the Super-Lorentzian
--T2b, -tSpecify the nominal T2 of the lineshape. During fitting in qi qmt scaling will be used to find the actual value. Should be specified in seconds.
--frq_count,--frq_start,--frq_spaceThese Control the position and number of samples to take on the lineshape.
frq_startandfrq_spaceshould be in Hertz.
qi qmt¶
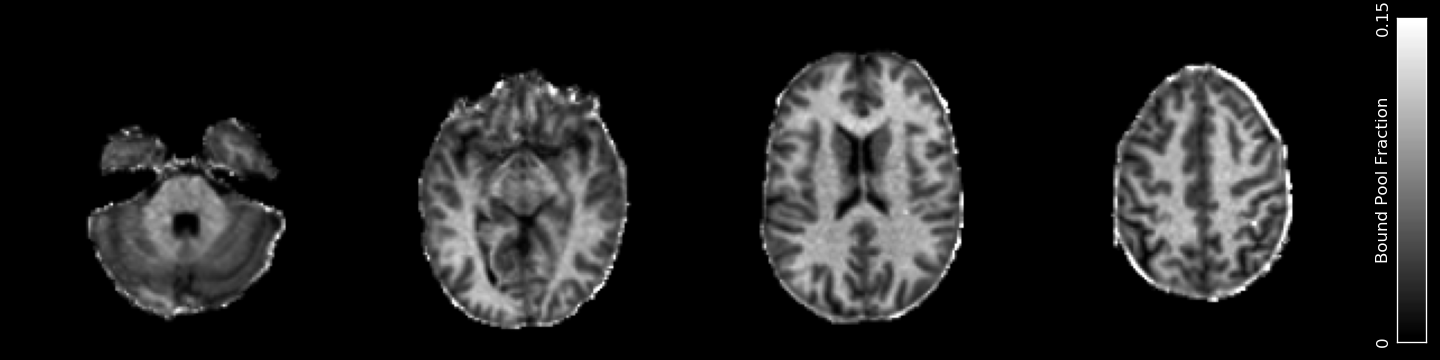
Calculates Quantitative Magnetization Transfer parameters using the Ramani model from steady-state gradient-echo data acquired with multiple off-resonance saturation pulses.
Example Command Line
qi qmt MTSatData.nii.gz --T1=T1.nii.gz --mask brain_mask.nii.gz --lineshape=superlorentz.json --B1=B1_map.nii.gz --f0=B0_map.nii.gz --json=input.json
Note that the T1 map argument is required input to stabilise the fitting.
Example JSON File
{
"MTSat" : {
"TR": 0.055,
"Trf": 0.015,
"FA": 5,
"sat_f0": [56360, 47180, 12060, 1000, 1000, 2750, 2770, 2790, 2890, 1000, 1000],
"sat_angle": [332, 628, 628, 332, 333, 628, 628, 628, 628, 628, 628],
"pulse": { "name": "Gauss", "bandwidth": 100, "p1": 0.416, "p2": 0.295 }
}
}
Trf is the pulse-width (RF Time). p1 and p2 are the ratio of the integral of \(B_1\) and \(B_1^2\) (the integrals of the pulse amplitude and the square of the pulse amplitude) to the maximum amplitude of the pulse. Both Trf and TR should be in seconds. sat_f0 is in Hertz. The bandwidth parameter is currently unused, any value will do.
Outputs
QMT_f_b.nii.gz- The bound pool fractionQMT_k.nii.gz- The fundamental exchange rate between poolsQMT_k_bf.nii.gz- The forward exchange rate from bound to free poolQMT_T1_f.nii.gz- T1 of the free poolQMT_T2_f.nii.gz- T2 of the free poolQMT_T2_b.nii.gz- T2 of the bound poolQMT_PD.nii.gz- The apparent Proton Density / size of the free pool
Important Options
--R1b, -rSpecify the relaxation rate of the bound pool. Default is 2.5 per second.
References
qi zspec_interp¶
Interpolates a Z-spectrum to arbitrary precision. Can output asymmetry values instead of a Z-spectrum.
Example Command Line
qi zspec_interp zspectrum.nii.gz --f0=LTZ_f0.nii.gz < input.json
The off-resonance map units must match the input frequencies (e.g. either PPM or Hertz)
Example JSON File
{
"input_freqs" : [ -5, -2.5, 0, 2.5, 5],
"output_freqs" : [ -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
input_freqs are the offset frequencies the Z-spectrum was acquired at. output_freqs are the frequencies you want the asymmetry calculated at.
Outputs
{input}_interp.nii.gzThe interpolated Z-spectrum.
Important Options
--f0, -fSpecify an off-resonance map. Units must be the same as the input & asymmetry frequencies.
-O, --orderThe order of Spline interpolation used. Default is 3 (cubic).
-a, --asymOutput asymmetry (:math`Z(+f) - Z(-f)`) values.
qi lorentzian¶
Fits sums of Lorentzian functions to a Z-spectrum. Highly customisable for the number of desired Lorentzian’s and their characteristics.
Example Command Line
qi lorentzian zspectrum.nii.gz < input.json
The Z-spectrum must be a 4D file with each volume acquired at a different offset frequency.
Example JSON File
{
"MTSat": {
"pulse": {
"p1": 0.4,
"p2": 0.3,
"bandwidth": 0.39
},
"Trf": 0.02,
"TR": 4,
"FA": 5,
"sat_f0": [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
"sat_angle": [180, 180, 180, 180, 180],
},
"pools" :
[
{
"name": "DS",
"df0": [0, -2.5, 2.5],
"fwhm": [1.0, 1.e-6, 3.0],
"A": [0.2, 1.e-3, 1.0],
"use_bandwidth": True
},
{
"name": "MT",
"df0": [-2.5, -5.0, -0.5],
"fwhm": [50.0, 35.0, 200.0],
"A": [0.3, 1.e-3, 1.0]
}
]
}
The input needs to include both the sequence parameters and the characteristics of the Lorentzian “pools” that you wish to fit. Currently the only important information used from the sequence are the saturation offsets, and optionally the bandwidth of the pulse. For each pool a name is required, and then triples of values representing the starting, lower and upper bound for the center frequency df0, the Full-Width Half-Maximum fwhm and amplitude A of the Lorentzian. You can also specify that the modified Lorentzian including the pulse bandwidth should be used “use_bandwith” : True. See the reference for details.
Important Options
--add, -aSpecify an additive model instead of the default subtractive (saturation) model. Useful when a base-line has already been subtracted from the Z-spectrum. See reference for details.
--zref, -zChange the reference value for the Z-spectrum. Default is 1.0, change to 0.0 for additive model.
Outputs
For each pool three outputs will be written, prefixed by the pool name. For a single pool representing direct-saturation (DS), the following will be written:
DS_f0.nii.gz- The center frequency of the fitted Lorentzian.DS_fwhm.nii.gz- The width of the fitted Lorentzian.DS_A.nii.gz- The amplitdue of the fitted Lorentzian.
References
qi mtr¶
Calculates Magnetization Transfer Ratio (MTR) and related quantities, e.g. MTasym and ihMTR.
By default only the MTR is calculated, assuming that the input contains one MT-weighted and one PD-weighted (reference) volume. However it can be used to calculate other quantities by passing in a JSON file specifying the formulas to calculate these. An example is given below to calculate MTR, ihMTR and MTasym from an acquisition with five volumes which correspond to ihMTw (+/-), ihMTw (-/+), PDw, MTw (+), MTw (-) where +/- correspond to applying the saturation pulse at positive or negative frequency.
Example Command Line
qi mtr mt_volumes.nii.gz --json=contrasts.json
Example JSON File
{
"contrasts": [
{ "name" : "MTR", "ref": [2, 2], "add": [3, 4], "sub": [], "reverse": true },
{ "name" : "MTasym", "ref": [2], "add": [3], "sub": [4], "reverse": false },
{ "name" : "eMTR", "ref": [2, 2], "add": [0, 1], "sub": [], "reverse": true },
{ "name" : "ihMTR", "ref": [2, 2], "add": [3, 4], "sub": [0, 1], "reverse": false }
]
}
The fields ref, add, sub refer to the indices of volumes that should be used as a reference, added or subtracted. reverse means that the contrast is reversed, i.e. it should be subtracted from the reference value before output (which is standard for MTR because it is a negative quantity).
Outputs
All outputs are expressed as percentages (multiplied by 100). By default there is one output:
MTR.nii.gz- The classic MTR, expressed as a percentage
If you use a custom contrasts file then the outputs will have the names specified in the .json file.
References
qi mtsat¶
Implementation of Gunther Helm’s MT-Sat method. Calculates R1, apparent PD and the semi-quantitative MT-Saturation parameter “delta”. This is the fractional reduction in the longitudinal magnetization during one TR, expressed as a percentage. Arguably could be included in the Relaxometry module instead. Outputs R1 instead of T1 as this is more common in the MTSat / MPM literature. If using multi-echo input data the input should be passed through qi mpm_r2s first and the output S0 files used as input to qi mtsat.
Example Command Line
qi mtsat PDw.nii.gz T1w.nii.gz MTw.nii.gz < input.json
Example JSON File
{
"MTSat": {
"TR_PDw": 0.025,
"TR_T1w": 0.025,
"TR_MTw": 0.028,
"FA_PDw": 5,
"FA_T1w": 25,
"FA_MTw": 5
}
}
Outputs
MTSat_R1.nii.gz- Apparent longitudinal relaxation rateMTSat_S0.nii.gz- Apparent proton density / equilibrium magnetizationMTSat_delta.nii.gz- MT-Sat parameter, see above.
References
qi ssfp_emt¶
Due to the short TR commonly used with SSFP, at high flip-angles the sequence becomes MT weighted. It is hence possible to extract qMT parameters from SSFP data. More details will be in a forthcoming paper.
Example Command Line
qi ssfp_emt ES_G.nii.gz ES_a.nii.gz ES_b.nii.gz
Outputs
EMT_T1f.nii.gz- Longitudinal relaxation time of the free water boolEMT_T2f.nii.gz- Transverse relaxation time of the free water poolEMT_M0.nii.gz- Apparent Proton DensityEMT_F.nii.gz- Bound pool fractionEMT_kf.nii.gz- Forward exchange rate
References